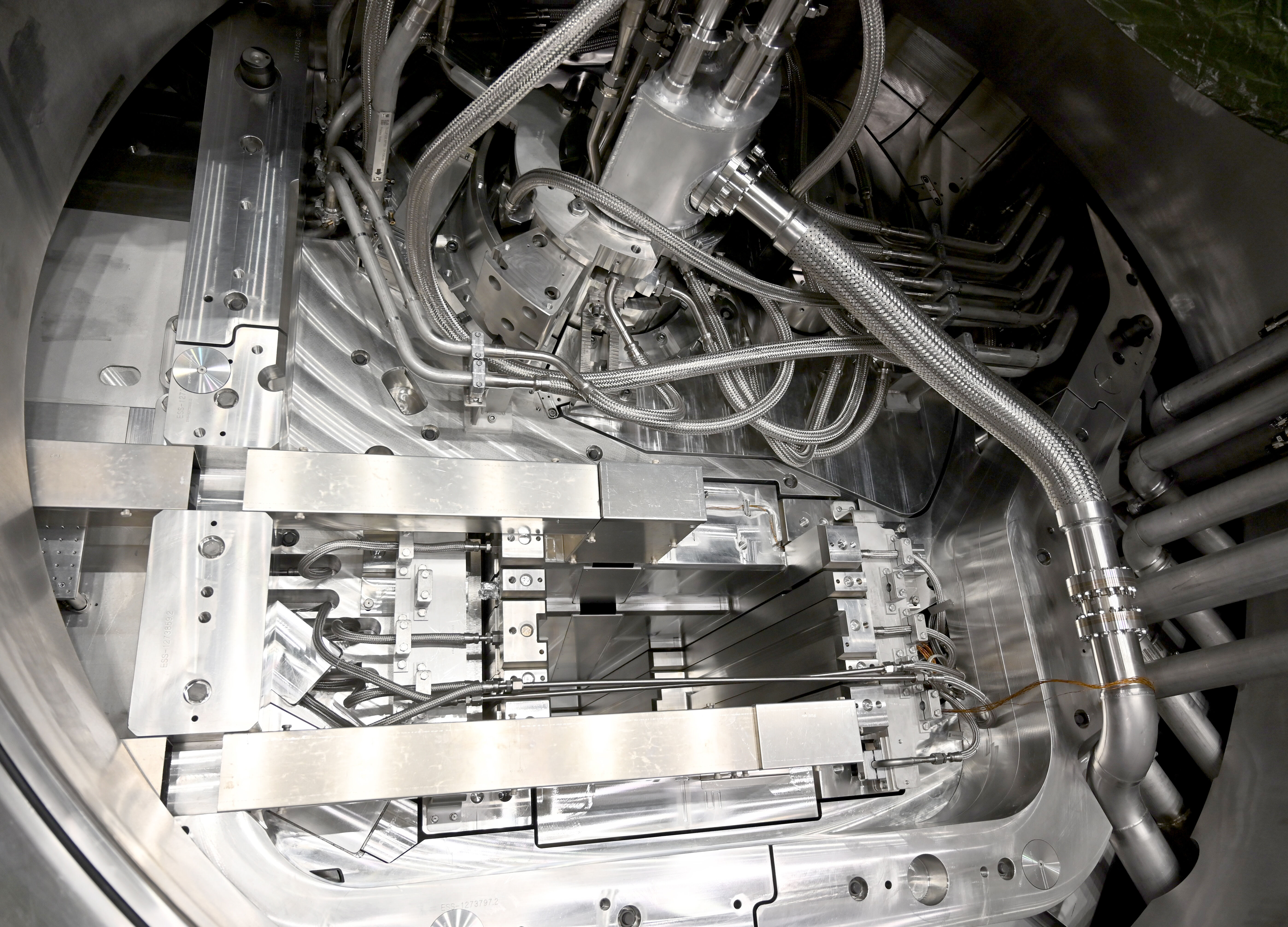
On 8 October, the GRID assembly was successfully installed, and the Target Station reached full hardware installation – an important step as ESS moves closer to sending the first protons onto the Target and producing neutrons for the first time.
Developed by the ESS Beam Instrumentation group, the GRID is a precision diagnostic system that measures key properties of the high-energy proton beam to ensure safe and stable operation. Together with the IMG (Imaging system) and APTM (Aperture Monitor), it forms part of the beam protection and monitoring system for the ESS Target.
While the APTM systems - installed at four locations along the accelerator - measure beam current and temperature, the GRID provides complementary diagnostics at the very end of the beamline, just before the beam hits the rotating Target Wheel. As the proton beam passes through the GRID, it generates signals that reveal the beam’s position, shape, and intensity, enabling precise alignment and focusing.
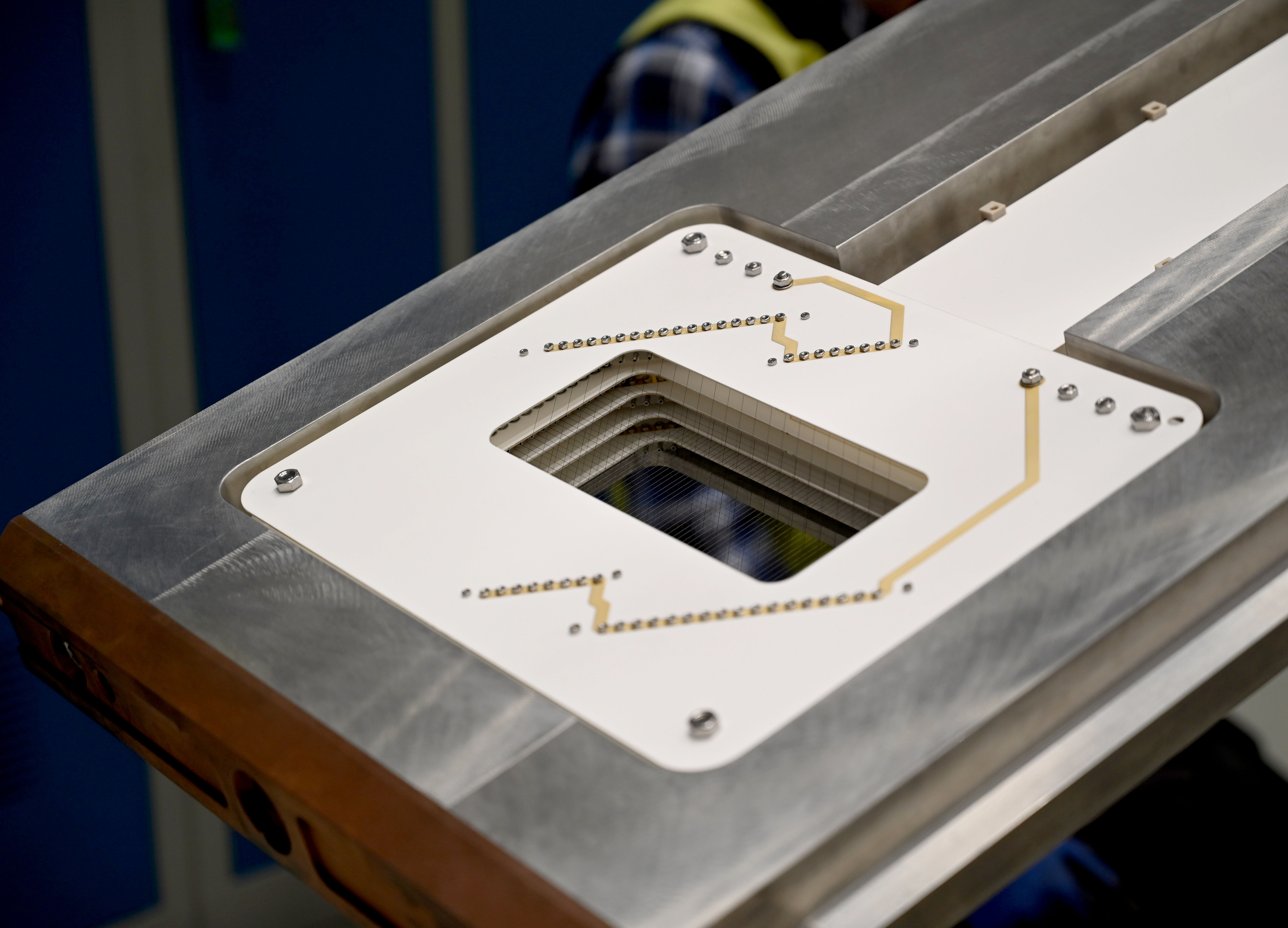
Carefully inserted into its dedicated slice of the Proton Beam Instrumentation Plug (PBIP) inside the Target Monolith (which contains the Target wheel), the GRID is a multi-wire harp profiling monitor, composed of thin silicon–carbide (SiC) wires arranged in 23 horizontal and 55 vertical strands. Additional wire planes generate electric fields that stabilise the measurement of the beam, by preventing nearby electrons from being absorbed.
Every microsecond, the system analyses the beam’s centre of mass and size in real-time. This information feeds into protective functions that ensure the beam remains within safe parameters, thus protecting the Target from excessive exposure or misalignment. The GRID is connected to the beam interlock system, which can automatically interrupt the beam if abnormal conditions are detected.